10 useful .NET 8 features for Sitecore C# developer
.NET 8 released in November last year. So, this blog post is a bit late but better late than never. Also, bumped into this wikipedia table about the list of .net version releases and associated support end date for different releases. So, this table should probably convey the importance of this post too.
Although there are many new features in .NET 8, the main purpose of this post is as a developer/blogger, I wanted to acquaint myself with the latest developer features useful on a day-to-day basis. So, in this process, I built my own examples for reference. Hope this is useful to you too and you enjoy this post.
To test the features, first setup a project that supports .NET 8.0. In case of any nuget packages added, they must be in 8.x to support the latest features.
1. JsonInclude for non-public properties:
Serialising/Deserialising C# objects to/from JSON string is part of any external application integration process. There seems to be a lot of enhancements in case of .NET 8 with regard to serialisation/deserialisation. One such feature is the ability of JsonInclude attribute to serialise/deserialise non-public members. Prior to .NET 8, only public properties could be decorated with this attribute.
Prior to .NET 8, such decoration throws an error as follows:
System.InvalidOperationException: 'The non-public property 'X' on type 'ConsoleApp2.MyPoco' is annotated with 'JsonIncludeAttribute' which is invalid.'
Usage:
//////
//////
Advantages:
- Better encapsulation of properties allowing value assignment through constructor
- Useful in passing calculated fields as part of json output
- Decorate C# properties with access modifiers like private,internal,protected, protected internal or private protected and the property will be automatically serialised.
Prior to .NET 8, stream-based overload was not present and only string-based destination file name was supported with syntax error as follows:
Error CS1503 Argument 2: cannot convert from 'System.IO.Stream' to 'string'
Create a zip stream for a directory input: From the stream create an unzipped directory in destination:
The ability to pass stream as a param is one of the advantages of these new methods:
////
4. Interface hierarchies:
Serialisation of inherited properties is possible with .NET 8. Here is an example to explain this feature better. Here is a hierarchical set of classes with interfaces.
Usage:
///////
/////
From .NET 8, json serialisation will look like this:
In other words, base class property values are retained in the child instance during serialisation.In other words, although the cats are correctly differentiated based on fur in the child instance, they both seem not to inherit legs base property important for animals.
5. JsonNamingPolicy for snake case and kebab case:
Prior to .NET 8 only camel-case was supported for JSON field serialisation:
- SnakeCaseUpper
- SnakeCaseLower
- KebabCaseUpper
- KebabCaseLower
Advantages:
- While integrating with external applications, although camelcase is predominantly used, a few applications have the other two naming conventions in use so, this support is useful for future
6. FrozenDictionary:
One of the interesting additions is the System.Collections.Frozen namespace that has the FrozenDictionary and this is useful if you want to load a list that wouldn't change after first time load. The FrozenDictionary offers faster traversal/retrieval of key/value pairs.
Prior to .NET 8, no such namespace:
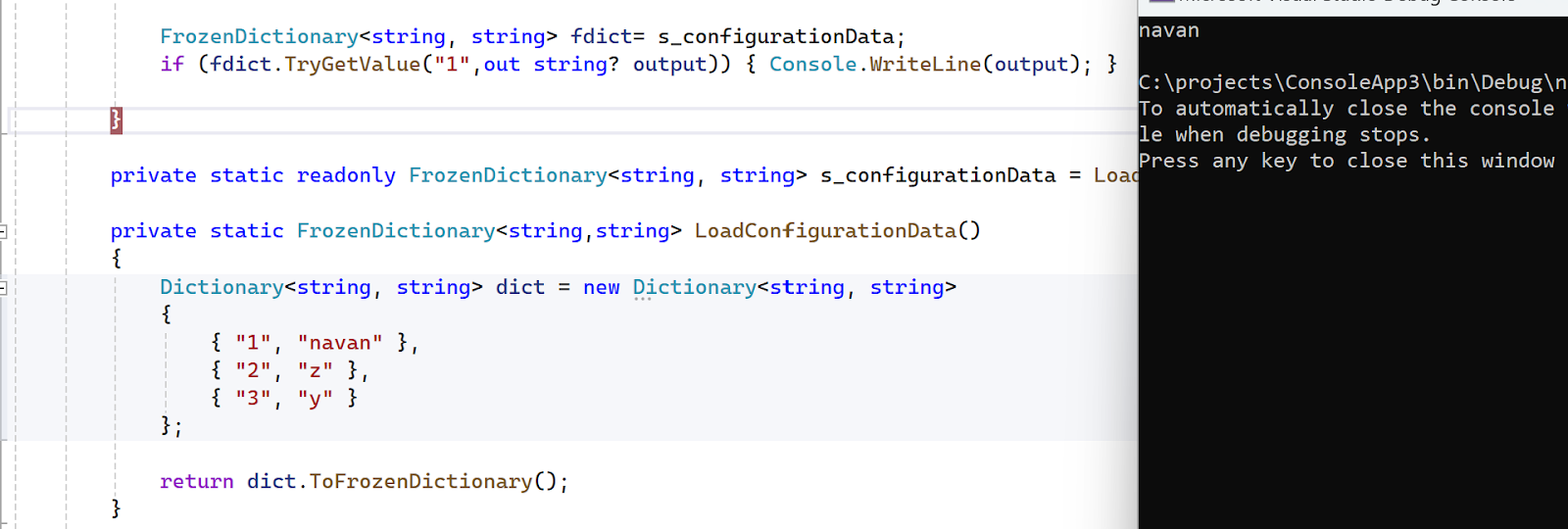
From .NET 8, Frozen is a namespace to utilise FrozenDictionary:
Usage:
/////////
////////
Method call:
Once the FrozenDictionary is retrieved, you can get value from the dictionary but can't add any more key/value pairs:
Trying to add a key/value pair fails after initial load since the dictionary is frozen:
System.NotSupportedException
HResult=0x80131515
Message=Specified method is not supported.
Source=System.Collections.Immutable
StackTrace:
at System.Collections.Frozen.FrozenDictionary`2.System.Collections.Generic.IDictionary<TKey,TValue>.Add(TKey key, TValue value)
at System.Collections.Generic.CollectionExtensions.TryAdd[TKey,TValue](IDictionary`2 dictionary, TKey key, TValue value)
Advantages:
- Better performance for large key/value pairs, could be useful to load Sitecore dictionary
7. Keyed DI services:
This again is one of the exciting new Dependency Injection features wherein when you have multiple implementations of the same interface, you can use any of those implementations by just passing the necessary key.
Usage:
For the sake of example, based on my earlier blog posts regarding different sitemap implementations for Sitecore MVP site that currently runs on .NET 8, I could provide keys and differentiate two different implementations and add it as part of the service collection:
Advantages:
- Flexibility in using multiple implementations of the same interface
- Might not require code changes in case of switching implementations if all implementations are identified and have keys before hand then, switching can be done by just passing the necessary key as a string from the config file






















Comments
Post a Comment